If you’re looking for guidance and tools to improve your use of AI in open-source intelligence investigations, look no further! This is a great roundup if you’re just starting with AI or want to expand its use in OSINT.
AI technology has radically changed how organizations and individuals use the internet. Since the release of ChatGPT, AI tools have witnessed a boost among internet users and companies alike. In the OSINT area, researchers have begun to use AI technologies to speed up the intelligence cycle.
In this article, I will discuss how AI tools can aid OSINT researchers in enhancing their capabilities during OSINT gathering activities. The article will mention use cases and give links to AI-powered tools that can help OSINT gatherers during their search. However, before we start, it is worth noting the main benefits of using AI in OSINT investigations.
How can AI technology assist OSINT gatherers in their work?
There are numerous cases when AI-powered tools can be leveraged in OSINT. Before I list some tools, let me introduce the various use cases that OSINT researchers can benefit by using AI-powered tools in their gathering activities:
Web scraping activities
AI techniques can be used to harvest large volumes of online data from various sources, such as social media platforms, blogs, discussion forums and deep internet databases. The collected information can be used later in different scenarios, such as tracking entities over time or monitoring public behaviors over some time. Machine learning models can be trained to harvest specific types of information, such as people's comments and replies on social media to extract them automatically.
Pattern recognition
Machine learning (ML) techniques can identify entities within large data sets: for example, analyzing a large number of files and finding linking relationships between different entities. Those entities could be an individual name, company name, address, email, phone number or any piece of data.
Content summary
Natural language processing algorithms can be used to summarize large sums of data. OSINT gatherers can use the summarization feature to analyze and extract information from datasets; for example, we can ask an AI summarization tool to extract all companies' names mentioned in a set of PDF files composed of hundreds of pages. In the same way, we can train the ML models to summarize a large amount of text or social media posts.
Sentiment analysis
A significant benefit of using AI technology is its ability to interpret human emotions through reading text (e.g., social media posts). OSINT researchers may not be able to accurately identify the emotional state of a particular user by merely reading what they write online (such as on their social media posts and comments). Another aspect is knowing the prevalent attitude of a group of people or society. For example, we can monitor internet users’ comments on social media platforms and customer reviews on online merchants about a specific brand or product to predict their future buying behavior. The same thing can be applied on a large scale (e.g., all people within a country) to understand their opinion about political, economic or sports matters.
Image recognition
Computer vision is a sub-type of AI that interprets digital media file information, such as images and video content. In the OSINT arena, computer vision can provide unparalleled power when conducting OSINT investigations involving analyzing digital media, such as:
- Face recognition: Identify a human face using AI and track their activities across different mediums, such as street surveillance cameras.
- Metadata analysis: Almost all digital files have some metadata. The manual process of extracting metadata from harvested digital files can be daunting. By using an AI solution, this task can be simplified a lot.
- Reverse image search: AI tools can speed up reverse image search significantly. It can also detect pictures produced using deep fake technology.
AI detection
AI technology is not used by good people only; threat actors have begun to utilize AI tools to facilitate criminals’ activities. AI technology can be used to detect content, such as images, videos and text, produced by AI tools.
The advantages of leveraging AI in OSINT tasks seem apparent; however, we must still consider the ethical and security (privacy) sides of using AI-powered tools to investigate and process sensitive data. This article will not cover the legal and privacy aspects; however, AI-powered tools should be used with caution when conducting online investigations for two main reasons:
- Avoid revealing the investigation or the investigator's identity.
- Avoid exposing sensitive information to the AI tools. For example, an investigator could upload a confidential file to ChatGPT to get a summary. ChatGPT is not fully private and may expose your uploaded files and text prompts used by investigators.
After we summarize the key areas where AI can be used in OSINT investigation, it’s time to mention some AI-powered tools that can help OSINT investigators in their research.
Searching the internet
AI-powered tools can speed up searching internet resources and return more accurate results. Some tools can be used to search within specific niches.
Tapesearch
Tapesearch is a service that searches within podcast transcripts. At the time of writing, the tool could search within 915,468 AI-generated transcriptions from 4,670 podcasts. The tool promises to add new transcripts every day.
DorkGPT
DorkGPT is a convenient tool for creating Google Dorks queries. All you need to do is provide your proposed search query using plain English, and the service will create the equivalent Google dork (see Figure 1).
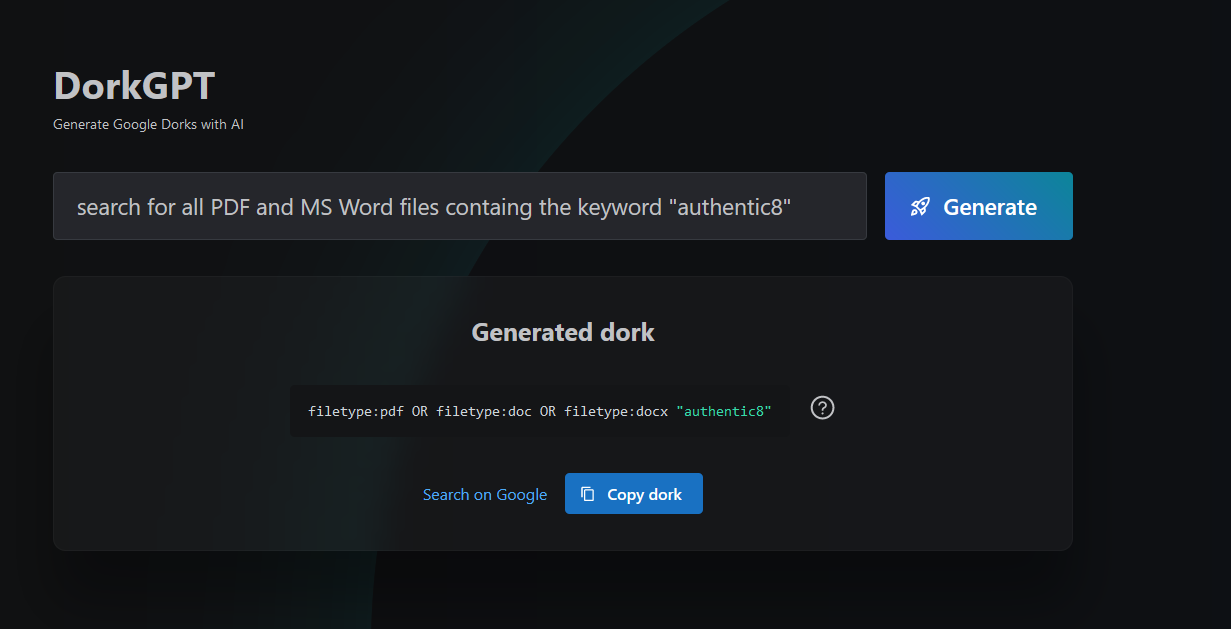
FIG 1 | Using DorkGPT to create Google dorks using AI technology
DorkGenius
The DorkGenius service is similar to DorkGPT; however, it can generate custom search queries for Google, Bing and DuckDuckgo (see Figure 2).
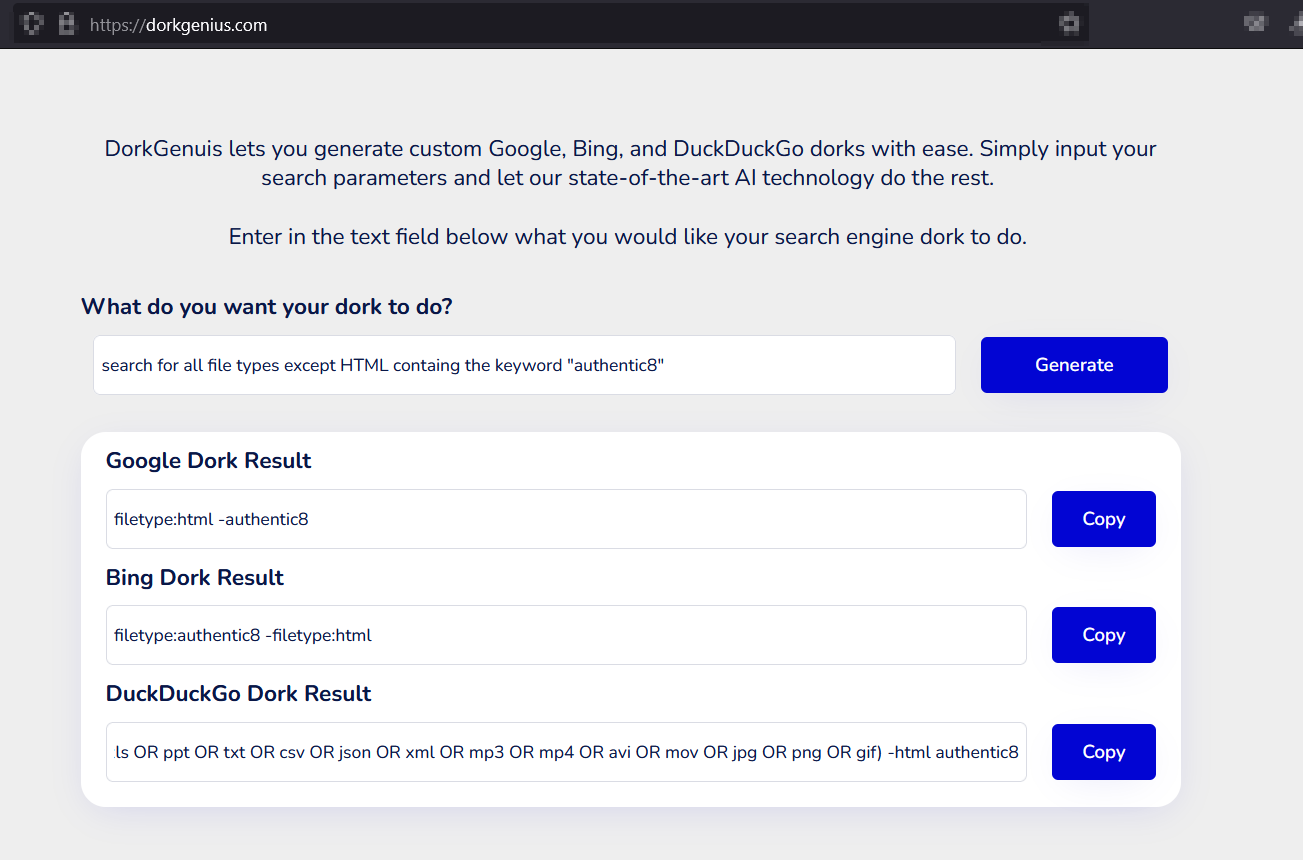
FIG 2 | dorkgenius utilizes AI to create custom search queries for major search engines
Google Word Sniper
The Google Word Sniper service uses AI to help locate the exact “keyword” on the Google search engine that is located:
- In the same title/headline (within an 8-word range)
- In the same sentence (within a 17-word range)
- In the same paragraph (within a 30-word range)
Explore AI
Explore AI is an AI-powered YouTube search engine that searches for answers directly from thousands of YouTube videos.
GitHub Data Explorer
GitHub Data Explorer is a unique AI-powered service for exploring GitHub event data. OSINT gatherers can use this service to ask natural questions about GitHub data, and the service will translate these questions into SQL queries. The results will be shown visually, which simplifies the interpretation of them. For example, I asked GitHub Data Explorer to fetch all projects related to keyloggers. The result is displayed in Figure 3.
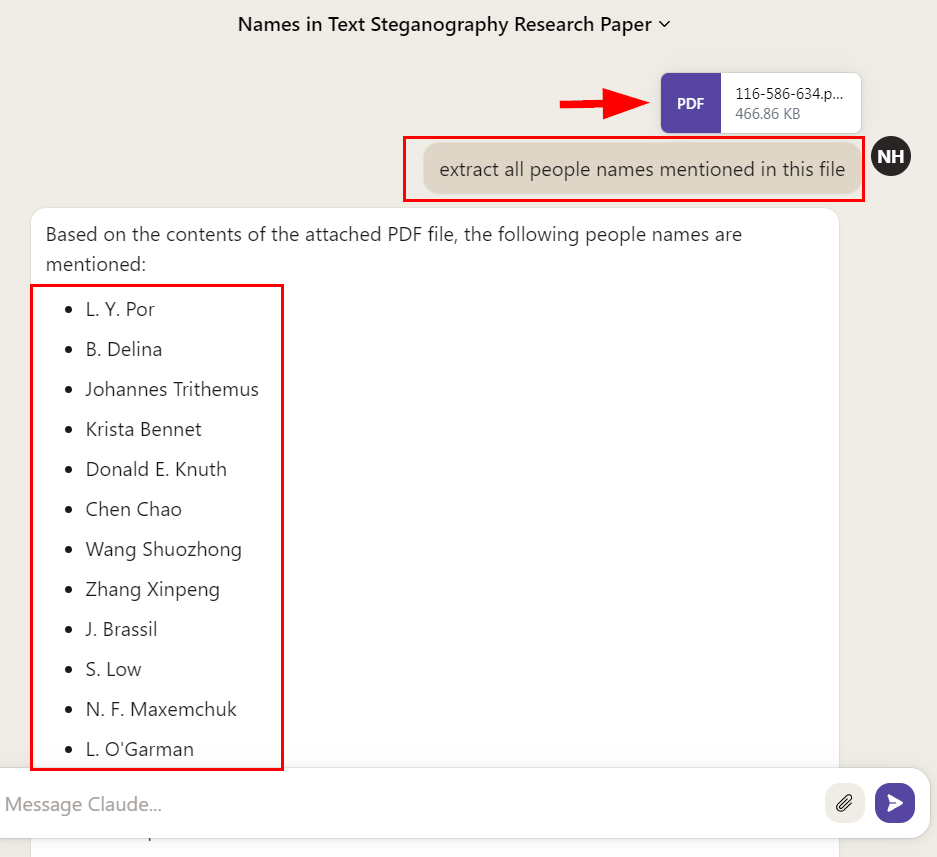
FIG 3 | GitHub Data Explorer translates users’ natural questions into complex SQL queries to fetch information from GitHub repositories
Summarizing contents
A regular task of OSINT gathering is searching within a large number of files for a specific name, address, place, phone or any keyword. Most programs, such as Acrobat Reader and MS Office Suite, provide a built-in search functionality; however, using AI is much faster, more accurate, and can easily analyze and extract information from these files. Here are some AI tools that can help you analyze large file contents.
Claude.ai
Claude.ai is another large language model (LLM) built by Anthropic that can analyze file contents. In Figure 4, I uploaded a PDF document and asked Claude to extract all the names mentioned within the file.
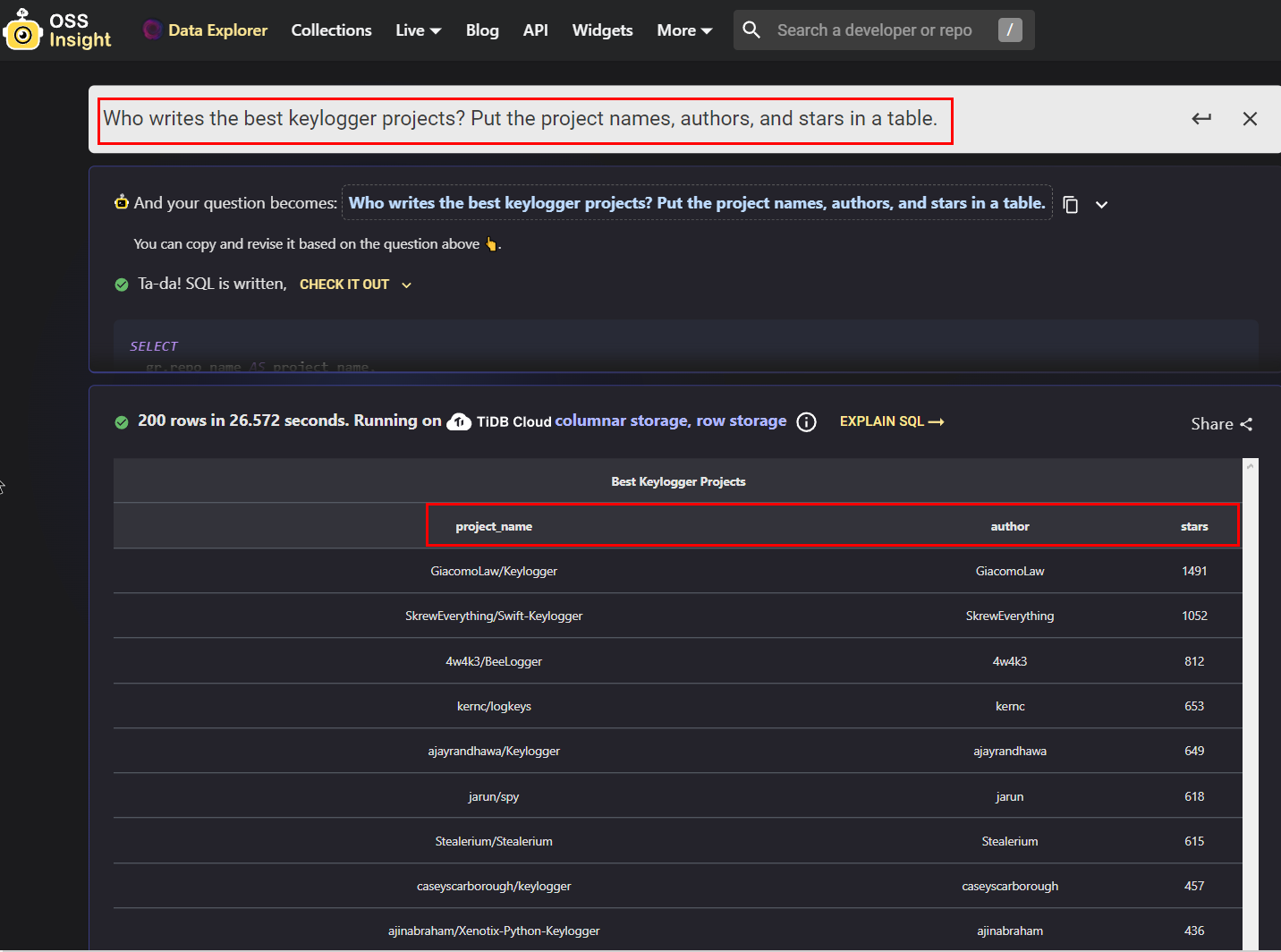
FIG 4 | https://claude.ai can easily extract people, companies and any entity name from uploaded PDF files
Chatpdf
Chatpdf is another AI tool for analyzing file contents, such as scientific papers, academic articles, and books. It can also analyze legal contracts, financial reports, manuals and training material. ChatPDF allows users to interact with the uploaded files and ask questions about their contents, similar to how we chat with ChatGPT.
Automated data collection
Web content is increasing at a rapid pace. For instance, millions of webpages and social media posts are created and added to the web jungle daily. Since the beginning of cyber OSINT, the major challenge was the sheer volume of data researchers must analyze carefully to find the desired results. Using AI tools, we can gather large amounts of data quickly and efficiently without requiring manual intervention by the researchers. Some OSINT use cases require collecting different types of data, such as server logs, financial transactions logs and data generated from Internet of Things (IoT) sensors. Utilizing AI-powered tools can aid in this endeavor.
There are many AI tools for scraping web content; most are commercial — you should always check their features and customer reviews before buying one. Here are two free services:
AnyPicker
AnyPicker is a free web data scraper comes as a Chrome extension.
Bardeen Scraper
The Bardeen Scraper service allows sending scraped web content into other applications (Google Sheets, Notion, or Airtabl) for analysis automatically and without writing any code.
Other popular AI-powered web scraping services are diffbot and Import.io.
Sentiment analysis tools
Most of these tools are commercial; however, there are still popular and reliable tools for performing sentiment analysis at no cost! Here are some popular free and open-source tools:
spaCy
spaCy is a free, open-source library for advanced natural language processing (NLP) in Python. It can help you build applications that can extract large-scale information from various sources or build natural language understanding systems.
NLP.js
NLP.js is a sentiment analysis package written in JavaScript. It can do both web scraping and sentiment analysis tasks.
Pattern
Another free web scraper and data sentiment library, Pattern can be trained to extract data from Google, Twitter and Wikipedia.
As the volume of digital data produced every second increases, traditional intelligence-gathering techniques will soon become insufficient. Leveraging AI-powered tools to gather and analyze data becomes a must. This allows OSINT investigators to focus their time on higher-level evaluation and assessment of intelligence rather than being overwhelmed by the lower-level tasks of finding and organizing relevant data. AI techniques like natural language processing, computer vision, and machine learning can help structure, parse and label the massive volume of unstructured data we can get during our investigations. Furthermore, AI technology shows promise for identifying manipulated or fake content, like doctored images and videos, fabricated news, and false social media engagement.


